Which one of the following is a bronsted lowry acid – Which one of the following is a Bronsted-Lowry acid? This question delves into the realm of chemistry, specifically the fascinating world of acids and bases. Bronsted-Lowry theory provides a fundamental understanding of these substances, guiding us through their properties and behaviors.
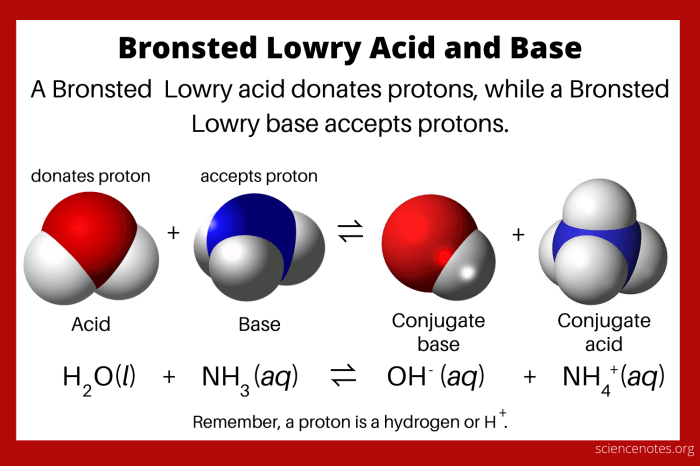
According to the Bronsted-Lowry theory, an acid is a substance that donates a proton (H+), while a base is a substance that accepts a proton. This theory offers a clear and concise definition of acids and bases, enabling us to identify and classify them accurately.
Bronsted-Lowry Acids: Definition and Characteristics
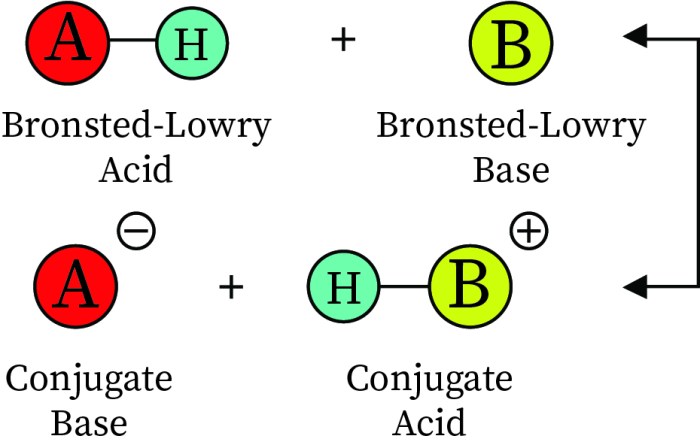
The Bronsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases, proposed by Johannes Bronsted and Thomas Lowry in the early 20th century, defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. According to this theory, an acid is a substance that can donate a proton (H+), while a base is a substance that can accept a proton.
Key characteristics of Bronsted-Lowry acids include:
- They donate protons (H+) in chemical reactions.
- They form conjugate bases when they donate a proton.
- They increase the concentration of H+ ions in solution.
Identification of Bronsted-Lowry Acids
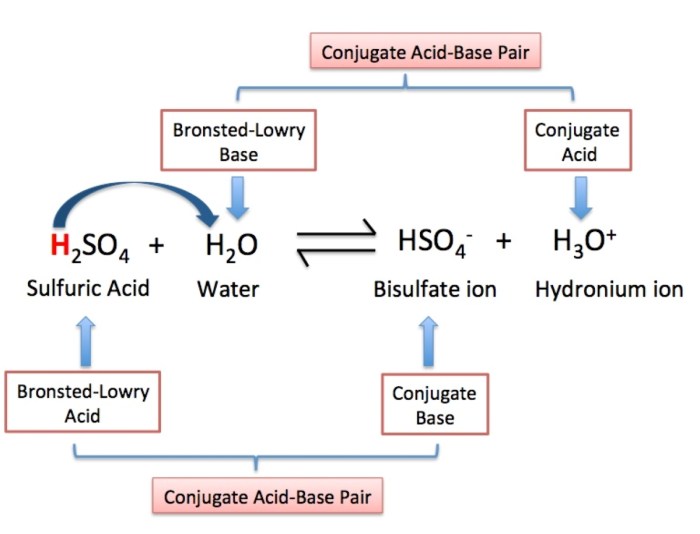
Common Bronsted-Lowry acids include:
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- Sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
- Nitric acid (HNO3)
- Acetic acid (CH3COOH)
- Hydrofluoric acid (HF)
Criteria for identifying Bronsted-Lowry acids:
- They contain hydrogen atoms that can be donated as protons.
- They react with bases to form salts and water.
- They turn blue litmus paper red.
Examples of Bronsted-Lowry Acids
| Acid | Formula | Conjugate Base |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrochloric acid | HCl | Cl- |
| Sulfuric acid | H2SO4 | HSO4- |
| Nitric acid | HNO3 | NO3- |
| Acetic acid | CH3COOH | CH3COO- |
| Hydrofluoric acid | HF | F- |
Types of Bronsted-Lowry acids:
- Strong acids: Completely dissociate in water, releasing all their protons (e.g., HCl, H2SO4).
- Weak acids: Partially dissociate in water, releasing only a small fraction of their protons (e.g., CH3COOH).
- Polyprotic acids: Can donate multiple protons in stepwise reactions (e.g., H2SO4, H3PO4).
Applications of Bronsted-Lowry Acids: Which One Of The Following Is A Bronsted Lowry Acid
Bronsted-Lowry acids have numerous applications, including:
- Chemistry: Acid-base reactions, titrations, pH regulation
- Biology: Metabolic processes, enzyme catalysis
- Industry: Production of fertilizers, plastics, dyes, batteries
FAQ Resource
What is the difference between a Bronsted-Lowry acid and a Lewis acid?
Bronsted-Lowry acids donate protons, while Lewis acids accept electron pairs.
What are some common examples of Bronsted-Lowry acids?
Hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and nitric acid (HNO3) are all common Bronsted-Lowry acids.
How can I identify a Bronsted-Lowry acid in a chemical equation?
Look for substances that donate protons or form conjugate bases.