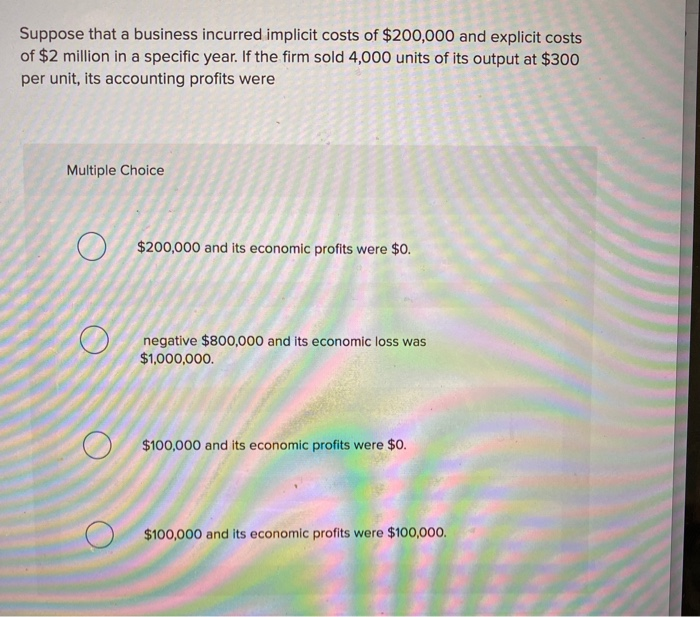
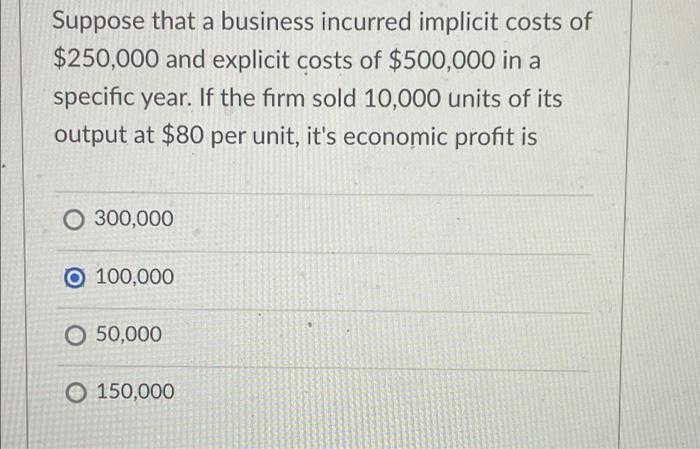
Suppose that a business incurred implicit costs of $1 million. What impact would this have on its decision-making and financial performance? Understanding implicit costs is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions and optimize their operations. This comprehensive guide delves into the significance, measurement, and management of implicit costs, providing valuable insights for business leaders.
Implicit costs, unlike explicit costs, are not directly reflected in financial statements but nevertheless represent real economic sacrifices made by businesses. They encompass the opportunity cost of resources used internally, such as the salaries of owner-managers or the value of foregone investment opportunities.
1. Identify Implicit Costs
Implicit costs represent the value of resources used in production that are not explicitly paid for by the business. They are often referred to as “opportunity costs” and play a significant role in business operations.
Examples of implicit costs include the value of the owner’s time spent working in the business, the use of personal assets (such as a home office), and the potential income that could have been earned if the resources were used elsewhere.
Implicit costs differ from explicit costs, which are direct monetary expenses incurred by the business, such as wages, rent, and raw materials.
2. Measurement of Implicit Costs
Measuring implicit costs can be challenging due to their non-monetary nature. However, there are methods for estimating these costs, such as opportunity cost analysis.
Opportunity cost analysis involves determining the value of the next best alternative use of the resources being used in production. For example, if the owner of a business is working in the business instead of working for another company, the implicit cost is the salary they could have earned elsewhere.
Assumptions and approximations are often necessary when measuring implicit costs. For example, the value of the owner’s time may be estimated based on their experience and industry benchmarks.
3. Impact of Implicit Costs on Decision-Making

Implicit costs influence business decisions by affecting the profitability and efficiency of operations. For instance, a business that underestimates implicit costs may make investment choices that appear profitable but actually result in losses.
Not adequately considering implicit costs can lead to biases and distortions in decision-making. For example, a business may prioritize projects with high explicit costs but low implicit costs, overlooking more profitable opportunities with higher implicit costs.
Real-world examples demonstrate the impact of implicit costs. Companies like Amazon have benefited from optimizing implicit costs through technology and automation, while others have suffered from underestimating or ignoring implicit costs.
4. Management and Optimization of Implicit Costs
Managing and optimizing implicit costs can enhance business performance. Strategies include utilizing technology and automation to reduce the need for labor and resources, and outsourcing non-core activities to minimize overhead costs.
It is crucial to evaluate the trade-offs between implicit costs and other factors, such as quality and efficiency. For instance, while outsourcing may reduce implicit labor costs, it may also impact product quality or customer service.
Businesses should regularly review and assess their implicit costs to identify areas for improvement and optimize resource allocation for enhanced profitability and efficiency.
Detailed FAQs: Suppose That A Business Incurred Implicit Costs Of
What are implicit costs?
Implicit costs are the opportunity cost of resources used internally by a business, such as the salaries of owner-managers or the value of foregone investment opportunities.
How do implicit costs differ from explicit costs?
Implicit costs are not directly reflected in financial statements, while explicit costs are expenses that are incurred and recorded in the financial records.
Why is it important to consider implicit costs in business decision-making?
Ignoring implicit costs can lead to biased and distorted decision-making, as businesses may underestimate the true cost of their operations.