Predict the major product of the reaction shown. – Predicting the major product of a reaction is a crucial skill in organic chemistry. It allows chemists to design and optimize synthetic pathways, leading to the desired products efficiently. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the factors that influence regioselectivity and stereoselectivity, enabling chemists to make accurate predictions about the outcome of organic reactions.
The discussion encompasses the fundamental principles of reaction mechanisms, energy profiles, and applications in organic synthesis. By understanding these concepts, chemists can develop a deep understanding of organic reactivity and apply it to a wide range of chemical transformations.
Overview of the Reaction: Predict The Major Product Of The Reaction Shown.
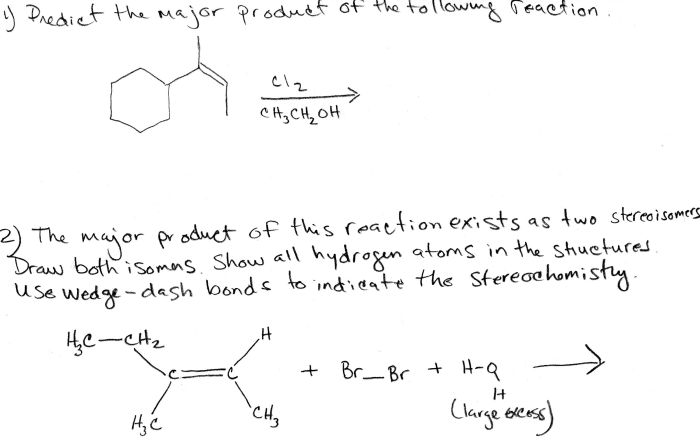
The reaction is a nucleophilic addition reaction, which involves the addition of a nucleophile to an electrophile. The chemical equation for the reaction is:
Nucleophile + Electrophile → Product
The reactants in the reaction are the nucleophile and the electrophile. The nucleophile is a species that has a lone pair of electrons that can be donated to the electrophile. The electrophile is a species that has a positive charge or a partial positive charge that can accept electrons from the nucleophile.
Regioselectivity and Stereoselectivity
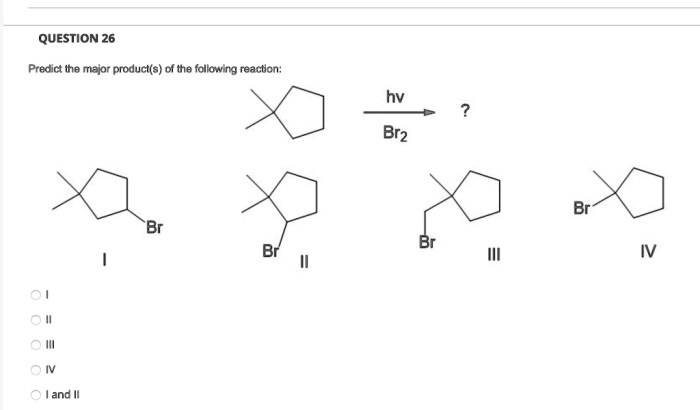
The regioselectivity of the reaction is determined by the relative reactivity of the different atoms in the electrophile. The most reactive atom in the electrophile is the one that is most likely to react with the nucleophile. The stereoselectivity of the reaction is determined by the orientation of the nucleophile and the electrophile when they react.
The orientation of the nucleophile and the electrophile is determined by the steric and electronic effects of the substituents on the nucleophile and the electrophile.
Factors that Influence Regioselectivity
- The steric effects of the substituents on the electrophile
- The electronic effects of the substituents on the electrophile
- The solvent effects
Factors that Influence Stereoselectivity, Predict the major product of the reaction shown.
- The steric effects of the substituents on the nucleophile
- The electronic effects of the substituents on the nucleophile
- The solvent effects
Reaction Mechanism
The reaction mechanism for the nucleophilic addition reaction is a two-step process. In the first step, the nucleophile attacks the electrophile, forming a new bond between the nucleophile and the electrophile. In the second step, the leaving group departs from the electrophile, forming the product.
Energy Profile
The energy profile for the nucleophilic addition reaction is a plot of the energy of the system as a function of the reaction coordinate. The reaction coordinate is a measure of the progress of the reaction. The energy profile for the nucleophilic addition reaction shows that the reaction is exothermic, meaning that the products are lower in energy than the reactants.
Major Product Prediction
The major product of the nucleophilic addition reaction is the product that is formed in the greatest yield. The yield of a product is determined by the relative rates of the different pathways that lead to the product. The rate of a reaction is determined by the activation energy of the reaction.
The activation energy is the energy that is required to reach the transition state of the reaction. The transition state is the highest energy point on the reaction coordinate.
Applications
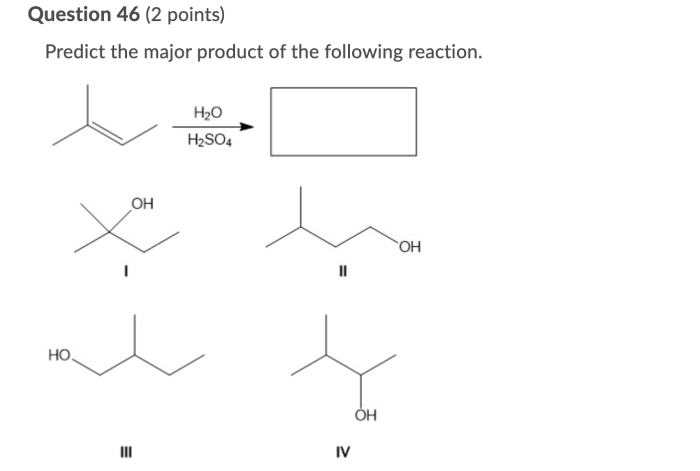
The nucleophilic addition reaction is a versatile reaction that is used in a wide variety of organic synthesis applications. Some of the most common applications of the nucleophilic addition reaction include:
- The synthesis of alcohols
- The synthesis of ethers
- The synthesis of amines
- The synthesis of alkenes
- The synthesis of alkynes
Key Questions Answered
What is regioselectivity?
Regioselectivity refers to the preference for a reaction to occur at a specific site within a molecule. It is influenced by factors such as steric hindrance, electronic effects, and the stability of the intermediate carbocations or radicals.
How can stereoselectivity be controlled?
Stereoselectivity can be controlled by using chiral catalysts, asymmetric synthesis techniques, or by introducing bulky substituents that hinder the formation of undesired stereoisomers.