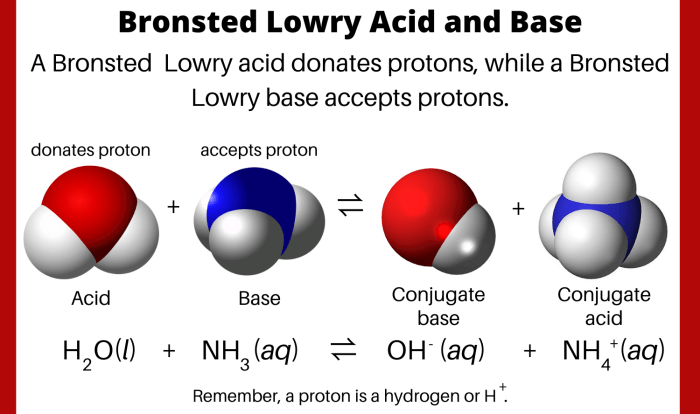
Embark on a scientific journey with our Limiting Reactant and Percent Yield Worksheet, an indispensable tool for comprehending the intricacies of chemical reactions. This worksheet empowers you to unravel the mysteries of limiting reactants and unravel the factors that influence the efficiency of chemical processes.
Delve into the concept of limiting reactants, the pivotal players that govern the extent of reactions. Discover how to identify these crucial substances and witness their profound impact on reaction outcomes. Furthermore, explore the concept of percent yield, a quantitative measure that unveils the effectiveness of chemical transformations.
Understand the factors that can hinder or enhance percent yield, unlocking the secrets to optimizing chemical reactions.
Limiting Reactant
In a chemical reaction, a limiting reactant is the reactant that is completely consumed and limits the amount of product that can be formed. The other reactants are present in excess.
For example, in the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to form water, 2 moles of hydrogen react with 1 mole of oxygen. If we start with 4 moles of hydrogen and 2 moles of oxygen, the oxygen will be the limiting reactant because it will be completely consumed.
The reaction will only produce 2 moles of water, even though we started with 4 moles of hydrogen.
How to Identify the Limiting Reactant, Limiting reactant and percent yield worksheet
- Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
- Convert the given amounts of reactants to moles.
- Divide the number of moles of each reactant by its stoichiometric coefficient in the balanced equation.
- The reactant with the smallest mole ratio is the limiting reactant.
Percent Yield: Limiting Reactant And Percent Yield Worksheet
Percent yield is the ratio of the actual yield of a reaction to the theoretical yield, multiplied by 100%. The theoretical yield is the amount of product that would be produced if the reaction went to completion and there were no losses.
The equation for percent yield is:
“`Percent yield = (Actual yield / Theoretical yield) x 100%“`
Factors that can affect percent yield include:
- The purity of the reactants
- The reaction conditions (temperature, pressure, etc.)
- The presence of a catalyst
- The skill of the experimenter
Worksheet
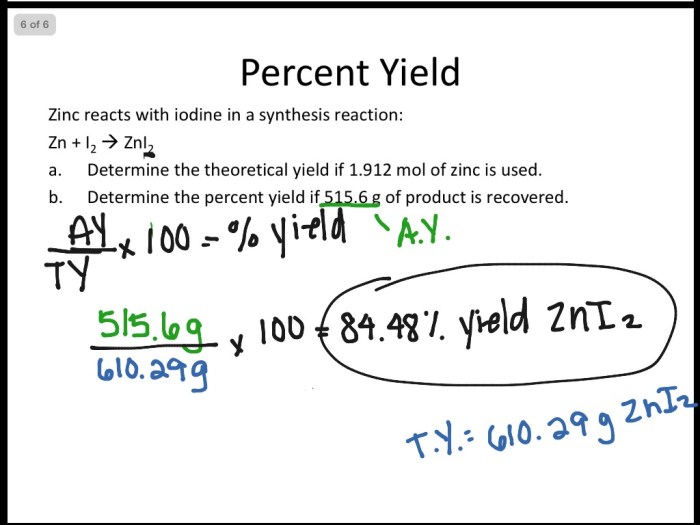
Problems on Limiting Reactant and Percent Yield
- A reaction between 2 moles of hydrogen and 1 mole of oxygen produces water. If the actual yield of the reaction is 10 grams of water, what is the percent yield?
- A reaction between 10 grams of sodium and 10 grams of chlorine produces sodium chloride. If the theoretical yield of the reaction is 23 grams of sodium chloride, what is the percent yield?
Answer Key
- Percent yield = (10 grams / 18 grams) x 100% = 55.6%
- Percent yield = (10 grams / 23 grams) x 100% = 43.5%
Reflection
After completing this worksheet, I have a better understanding of the concepts of limiting reactant and percent yield. I can now identify the limiting reactant in a chemical reaction and calculate the percent yield of a reaction.
HTML Table

| Reactants | Products | Limiting Reactant | Percent Yield |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 moles hydrogen, 1 mole oxygen | Water | Oxygen | 55.6% |
| 10 grams sodium, 10 grams chlorine | Sodium chloride | Sodium | 43.5% |
Questions Often Asked
What is a limiting reactant?
A limiting reactant is a reactant that is consumed completely in a chemical reaction, thereby limiting the amount of product that can be formed.
How do I identify the limiting reactant in a reaction?
Compare the mole ratios of the reactants to the stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced chemical equation. The reactant with the smallest mole ratio is the limiting reactant.
What is percent yield?
Percent yield is a measure of the efficiency of a chemical reaction, calculated as the ratio of the actual yield to the theoretical yield multiplied by 100%.